NIROSETI Description
The Near-Infrared Optical SETI (NIROSETI) instrument is the first instrument of its kind designed to search for signals from extraterrestrials at near-Infrared wavelengths. The near-infrared regime is an optimal spectral region to search for signals from extraterrestrials, since it offers a unique window for interstellar communication with less interstellar extinction than in the visible regime.
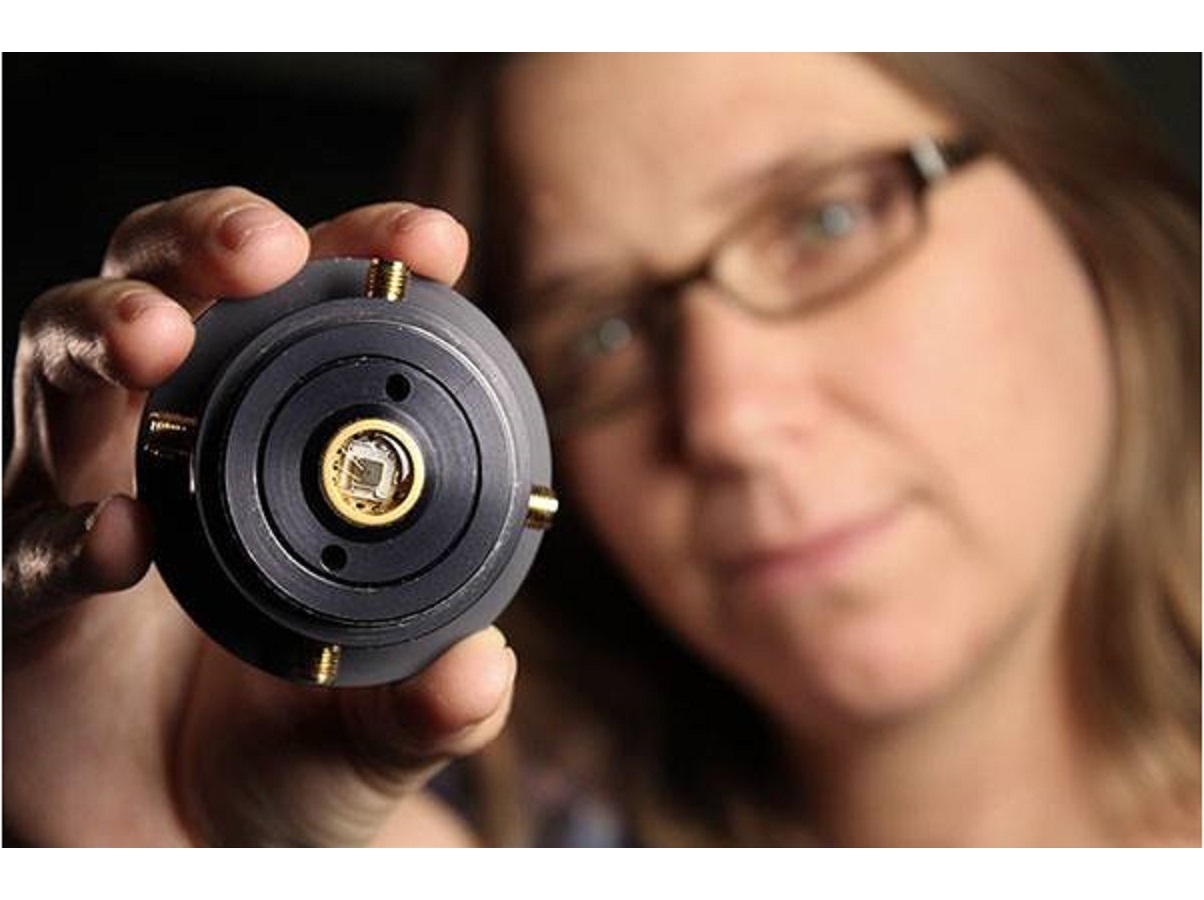
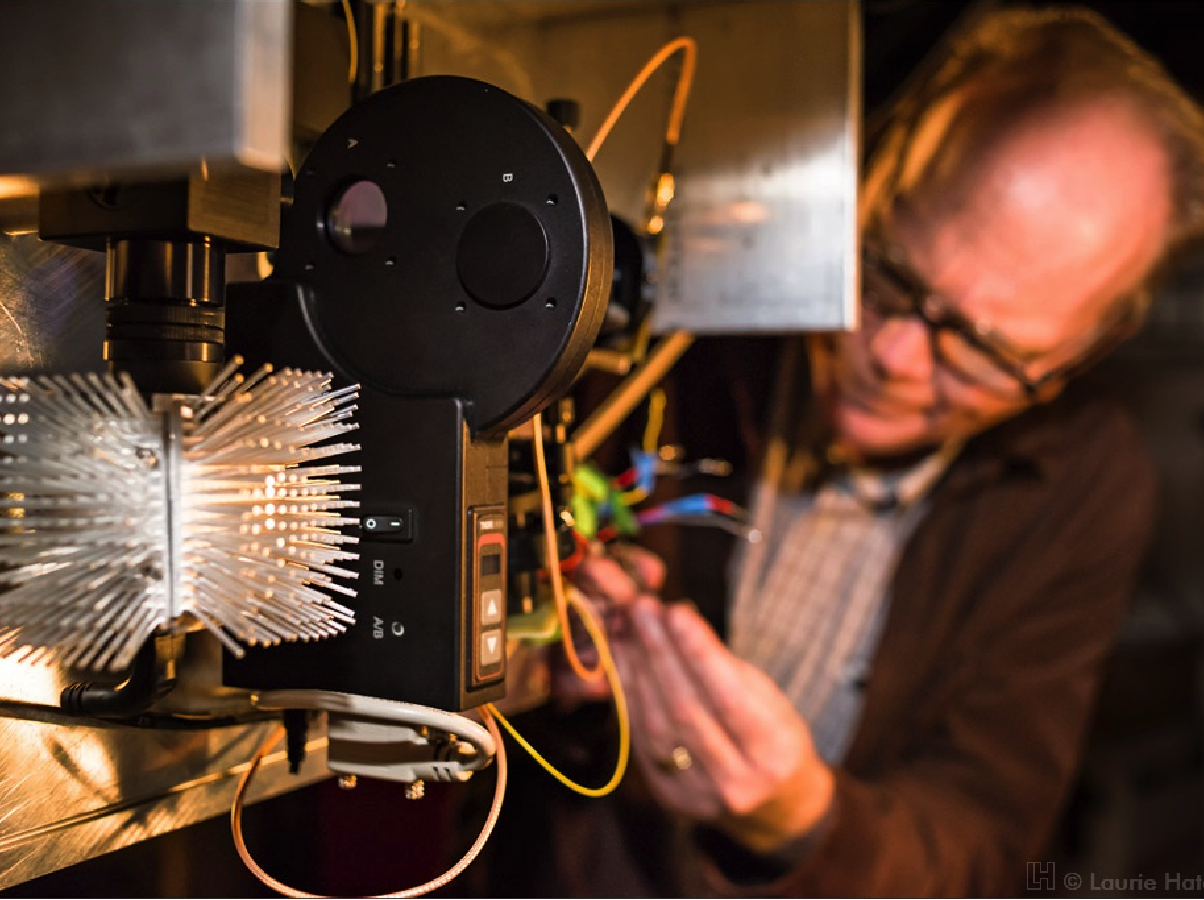
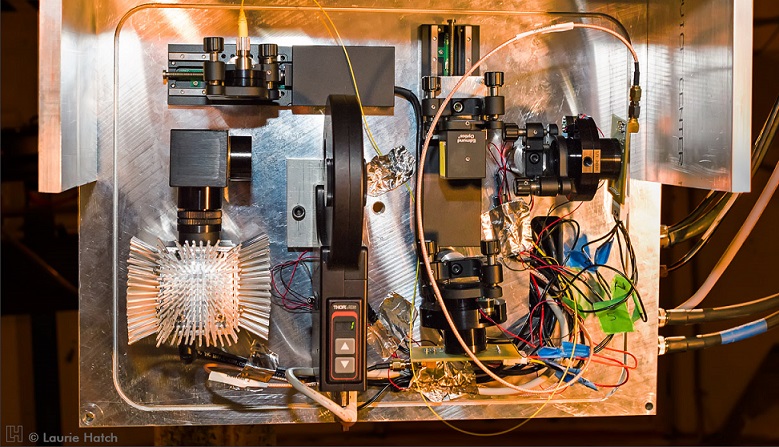
The NIROSETI instrument utilizes two near-infrared (950 - 1650 nm) discrete amplification Avalanche Photodiodes (APD), each with > 1 GHz bandwidths and low noise characteristics, to be able to detect artificial, very fast (nanosecond) pulses of infrared radiation.
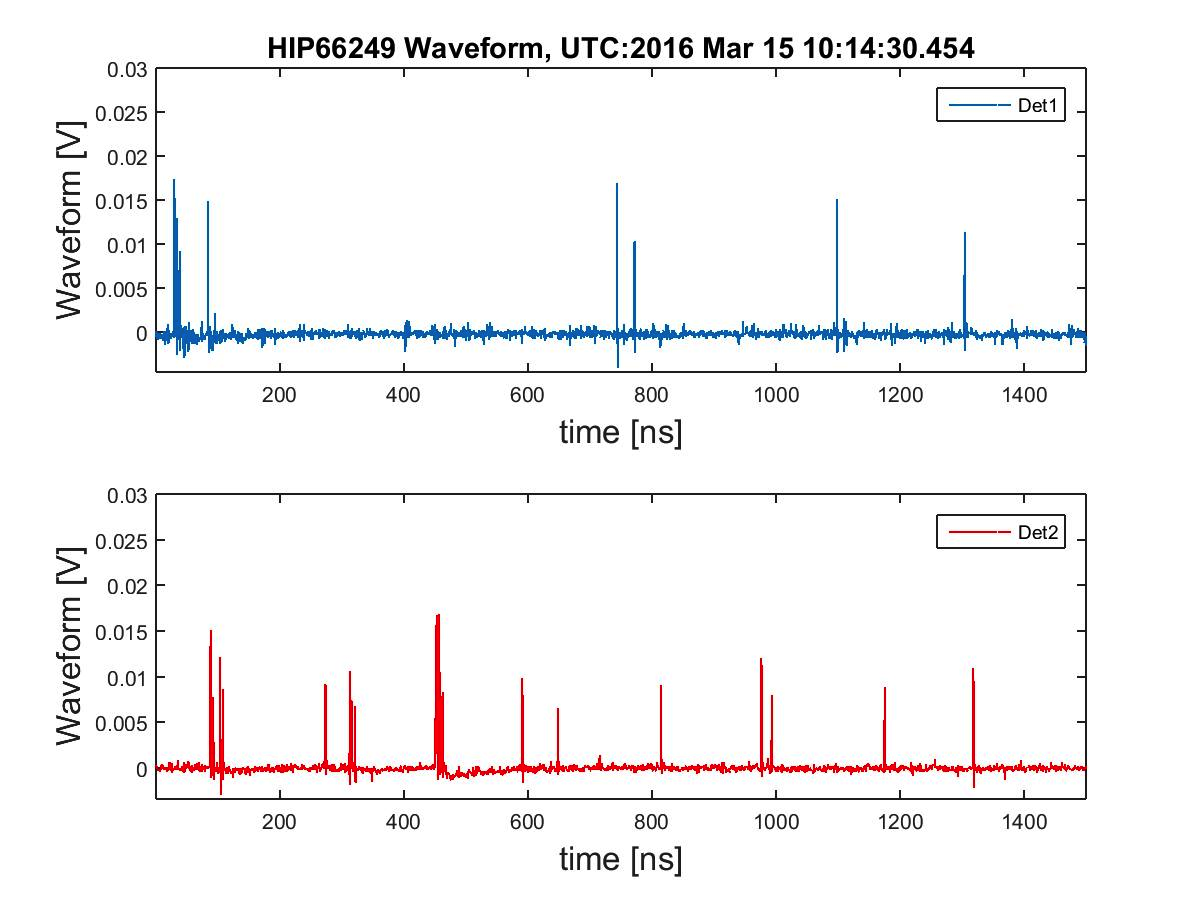
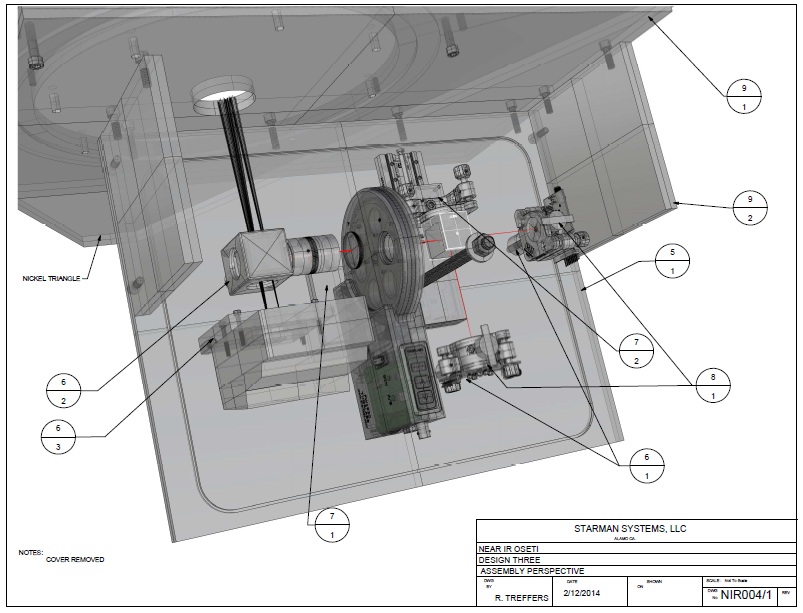
The NIROSETI instrument, which is mounted on the Nickel 1-m telescope at Lick Observatory, splits the incoming near-infrared light onto two channels, and then uses APDs to check for coincident events, which indicate signals that are detected by both detectors simultaneously.
NIROSETI Details
First light on March 14th, 2015
Observing about 2,000 celestial objects
High-speed infrared detectors working in coincidence
High-time resolution Astronomy