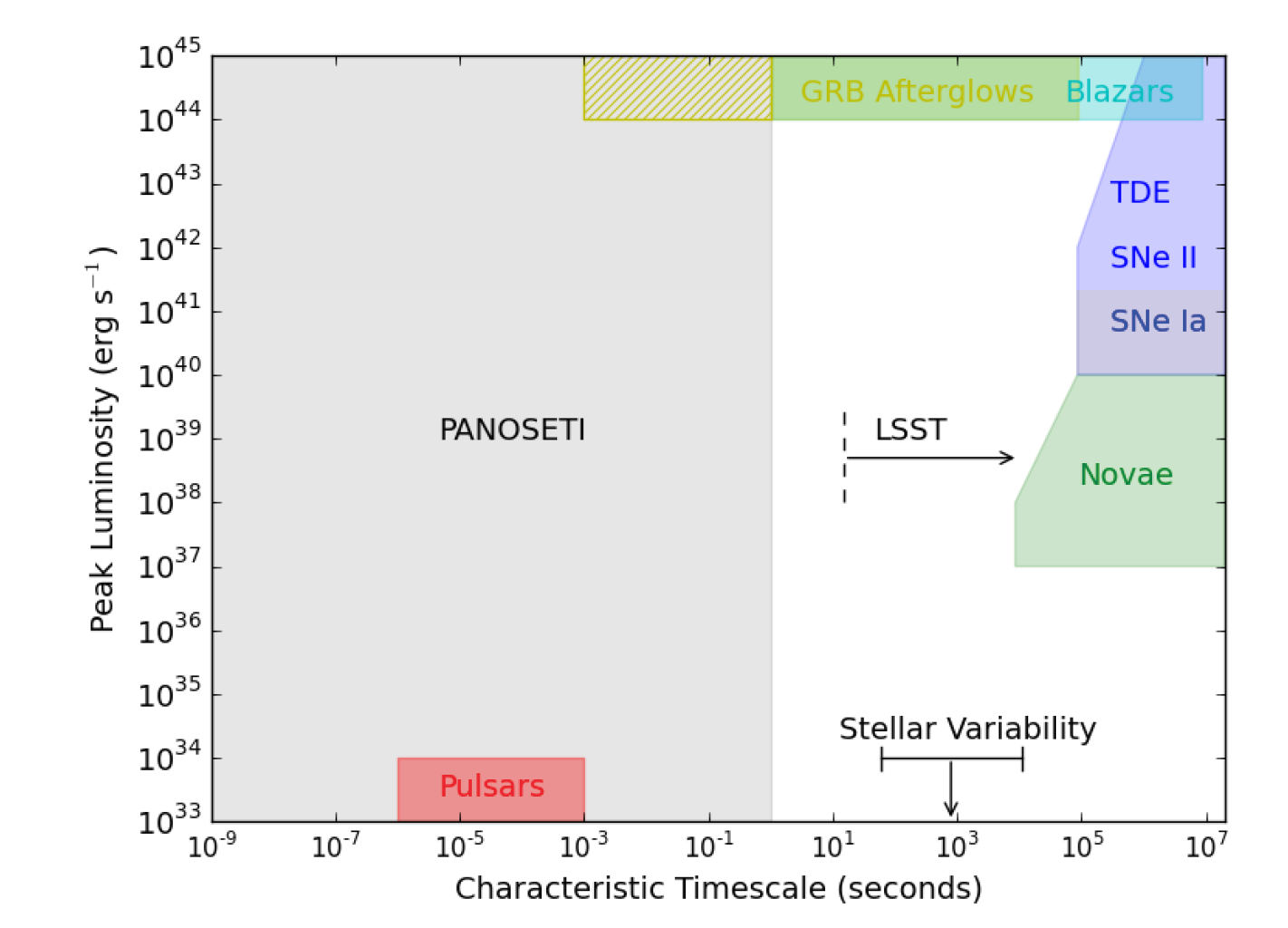
Fast time resolutions (nano-seconds to seconds) have barely been explored and represents an observational limit with current ground and space-based facilities, especially since facilities are unable to represent large sky coverage with high duty cycles. Even with these limitations, new flavored transient sources are being found at shorter timescales (seconds), e.g., ASASSN-15lh. GRB afterglows can be observed for seconds to hours after the initial triggering event, but there have been no known observations that extend down to milli-seconds to seconds for rapid follow-up (hatched area). GRB 080319B, the brightest recorded GRB in 2008, resides above the y-axis at 1051 erg s-1. Stellar variability from cataclysmic variables, Cepheids, stellar ares are typically less than 1034 erg s-1. PANOSETI will be capable of exploring luminous transient and variable phenomena from nanoseconds to seconds (grey area).
>